On July 3, the Ministry of Commerce and the General Administration of Customs issued the "Announcement on the Implementation of Export Control of Gallium and Germanium Related Items" (hereinafter referred to as the "Announcement"), which pointed out that in accordance with the relevant provisions of the Export Control Law of the People's Republic of China, the Foreign Trade Law of the People's Republic of China and the Customs Law of the People's Republic of China, in order to safeguard national security and interests, with the approval of The State Council, It is decided to implement export control on gallium and germanium related items, and items that meet the relevant characteristics shall not be exported without permission, and the announcement will be officially implemented from August 1, 2023.
What is the use of either substance? At present, gallium consumption areas include semiconductor and photoelectric materials, solar cells, alloys, medical devices, magnetic materials, etc., of which the semiconductor industry is currently the largest consumption area of gallium, accounting for about 80% of the total consumption, and germanium as an equally important semiconductor material, In semiconductor, aerospace measurement and control, nuclear physics detection, optical fiber communication, infrared optics, solar cells, chemical catalysts, biomedicine and other fields have a wide range of important applications.

It can be said that gallium and germanium have an indispensable role in the semiconductor industry, although both are not rare earth elements, the output is not high, but the first production country is China, according to the report of the United States Geological Survey, China is the world's largest gallium and germanium producer, accounting for more than 95% of the global gallium production, germanium production of more than 67%. Between 2018 and 2021, 53% of US gallium imports and 54% of germanium imports came from China.
In fact, although the reserves of gallium in the United States are low, the reserves of germanium are not low, and the total proven reserves of germanium in the world are about 8,000 tons, and the United States accounts for 3,800 tons, ranking first in the world, while gallium is also distributed in the world
Many people may have such doubts in their minds: After the country issued export controls on gallium and germanium related items, other countries, including the United States, can also choose to produce the two metals themselves and get rid of their dependence on Chinese materials.
Such an idea can not be said wrong, but gallium and germanium can not be speculated with such a simple idea, the door behind them is not much simpler than TSMC to produce a 4nm chip.
Indispensable material
First of all, gallium and germanium belong to sparse metals, which are characterized by extremely low crustal abundance, extremely dispersed in rocks, and difficult to enrich. Some people even believe that they cannot form "independent deposits". These characteristics also determine that their enrichment requires special ore-forming conditions and controlling factors. Its metallogenic theory, prospecting model and exploration technology are not exactly equivalent to other types of deposits.
Although gallium is the most abundant sparse metal in the earth's crust (15μg/g), it has the fewest independent minerals. Only two independent minerals, CuGaS2 and Ga(0H)3, are found in the Tsumeb lead-zinc deposit in South Africa, and most of them exist in the form of associated metals. At present, most of the gallium discovered is associated with bauxite deposits, mainly distributed in Africa, Oceania, South America, Asia and other places.
In the early 1960s, gallium began to attract the attention of various countries. Gallium arsenide as a new high-quality semiconductor research heat rise, with the excellent performance of gallium arsenide compounds used as semiconductor materials continue to be discovered, gallium arsenide is also widely used in microwave devices, lasers and light-emitting diodes and other products.

Gallium-related products, gallium nitride (GaN) is one of the most representative of the third generation of semiconductor materials, is the world's most advanced semiconductor materials, and gallium arsenide (GaAs) is the representative of the second generation of semiconductor materials, in the high frequency, high speed, high temperature and anti-irradiation and other microelectronics device development occupies a major position.
In terms of country production, China's gallium production is the highest in the world. Germany and Kazakhstan ceased gallium production in 2016 and 2013, respectively (Germany announced in 2021 that it would restart primary gallium production by the end of the year), Hungary and Ukraine ceased gallium production in 2015 and 2019, respectively. In 2020, there are only three countries producing crude gallium from mine raw materials in the world, namely China, Japan, South Korea and Russia, and China, as the world's largest producer of crude gallium, accounts for more than 90% of global production by 2021.
As mentioned earlier, gallium mainly exists as an associated ore of bauxite, which leads to the fact that we will not produce gallium alone, but a by-product of refining alumina in the trend, statistics show that China's production of refined alumina accounts for only about half of the world, so why in the production of crude gallium, China can use 50% of the production capacity to do it alone?
The reason is very simple, no one does not make money on the loss of trading, in the value of gallium can be discovered, the price of crude gallium in the market has been steadily declining, which leads to few alumina companies willing to expand production to refine gallium. In the 1970s, the price of gallium was as high as $3,000 per kilogram, and the production of gallium reached a historical peak of 575 tons in 2015, but the price was only $200-300 per kilogram, and after several years of low prices have made a lot of European and American alumina companies withdraw from the market.
This also brings a problem, the short-term rise in gallium prices, simply can not attract those companies to re-open refining gallium plants, because the cost of building the plant is far more than this part of the difference, in case the price falls after the completion of the plant, this part of the passion to open the plant enterprises then want to cry
Of course, state intervention is also one way to solve the problem. On March 9, the United States and the European Union moved forward with the drafting of a trade agreement focused on critical minerals, the "Critical Minerals Club" initiative, which aims to exclude China's influence on the supply of critical minerals.
However, gallium is subject to export restrictions, the most anxious is not the United States and the European Union, but across the sea in Japan, due to Japan's semiconductor industry developed, the annual consumption increase is larger, is the first consumer of gallium resources, as of 2013, Japan's consumption of gallium reached 97 tons, mainly relying on imports and recycled gallium (gallium resource recovery), and the main source of imports is of course China.
As far as the current situation is, refining technology and refining facilities can not be built overnight, there is ready gallium can be bought, no one is willing to spend great efforts to exploit at a loss, large-scale spot only from China to buy this way, the United States, the European Union and Japan are not spared.
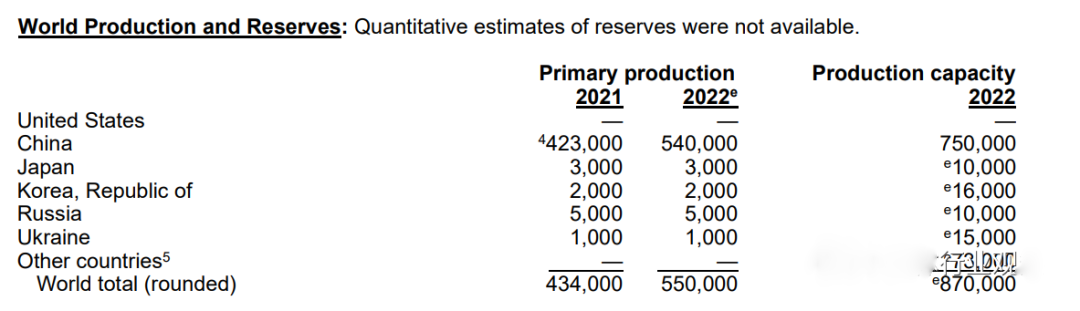
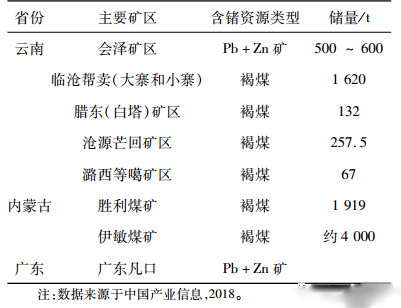
Speaking of germanium, compared with gallium, there are some details of the difference, germanium in the crust content of 1.5μg/g, it is difficult to independent mineralization, generally distributed in a dispersed state in other minerals composed of elements. Germanium-bearing deposits can be divided into "coal type" germanium-bearing deposits and "lead-zinc type" germanium-bearing deposits, so industrial germanium mainly comes from lead-zinc deposits and Germanium-rich coal byproducts.
At present, the world's proven germanium reserves are only 8600 tons, mainly distributed in China, the United States and Russia, of which the United States retains reserves of 3870 tons, accounting for 45% of the global content, followed by China, accounting for 41% of the world. In the United States, germanium bearing deposits are mainly distributed in Alaska, Tennessee and Washington State, mainly lead and zinc deposits. Germanium bearing deposits are mainly found in Inner Mongolia and Yunnan, both in lead-zinc deposits and coal mines. Russian germanium deposits are mainly distributed in the Far East and Siberia, mainly in coal mines.
According to the characteristics of germanium, three main uses have been developed: First, germanium has a high infrared refractive index, wide infrared transmission band range, small absorption coefficient, low dispersion rate, easy processing and corrosion resistance, and is very suitable for making germanium single crystal for infrared optical lenses and infrared optical Windows.
Secondly, germanium-doped fiber has the advantages of large capacity, small light loss, low dispersion, long transmission distance and no environmental interference. GeCl4, as an important dopant for making fiber prefabricated rods, can improve the refractive index of the fiber core, expand the transmitted light to a longer wavelength region, greatly improve the transmission efficiency of the fiber and reduce energy consumption.
Finally, germanium can also be used to make germanium substrate gallium arsenate solar cells, such cells have high efficiency, high voltage, good temperature resistance and other characteristics, its energy conversion rate of up to 50%, far more than the traditional polycrystalline silicon (17%~19%) and thin film cells (6%~13%), is widely used in space photovoltaic and ground photovoltaic field.

As mentioned above, unlike gallium, China's germanium reserves, and there is no overwhelming advantage, the United States has proven germanium reserves ranked first in the world, but in production is far less than China, the United States began to import a large number of germanium in 2013, basically abandoned the mining of crude germanium, only responsible for refining.
Many people think that the United States is protecting its strategic resources, but it is not.
Although the United States is the world's largest germanium reserves, but its germanium resources are mainly associated with lead and zinc ore, germanium can produce much, all see the production of lead and zinc mine, want to improve the production capacity of germanium, you have to wantonly mining lead and zinc, and lead and zinc as heavy metals, mining pollution is not small, a sharp increase in production capacity, may also cause pollution to groundwater.
Germanium is not much more optimistic than gallium, once China, as the largest exporter, opens export controls, the United States and Japan, which have a high consumption of germanium, will be greatly affected, and can not establish a suitable supply channel in a short time.
More importantly, China, as the fastest developing country in semiconductor, communications, photovoltaic and other industries, has not low demand and consumption of gallium and germanium, two kinds of rare and loose metals, while domestic bauxite and gallium-containing lignite have shown signs of depletion after years of mining, and appropriate export contraction can also help domestic enterprises adapt to the future of low-grade raw materials. This interferes with the push to develop lower cost metal extraction processes.
Now the export control of gallium and germanium, from another point of view, is also a means to let the industry from primary to high-end development, the resource advantage into an industrial advantage.
De-globalization and re-globalization
In June this year, Tsinghua University professor Wei Shaojun delivered a speech on the "re-globalization of the semiconductor industry" at the Integrated Circuit Forum, which released a lot of data on domestic semiconductors, it is worth noting that although the value share of domestic chips rose from 13% in 2013 to 41.4% in 2022, But as a key goal of the "Made in China 2025" initiative, the semiconductor self-sufficiency rate will still not reach 70% by 2025.
He emphasized that the accelerated growth of China's semiconductor manufacturing industry over the past decade was mainly driven by the fabs operated by foreign companies in China. From 2016 onwards, the average compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of semiconductor companies owned by local investors in China was 14.7%. However, non-Chinese wafer manufacturers from Taiwan, South Korea and elsewhere are growing at a higher CAGR of 30 per cent. This not only doubles the expansion rate of China's semiconductor industry, but also highlights the continued dependence of China's semiconductor manufacturing industry on external manufacturers.

It can be said that the domestic semiconductor industry has benefited from the development of globalization and has been able to play an important role in the global semiconductor industry after the arrival of the new century, and the investment and demand from all over the world have allowed domestic semiconductor companies to take the east wind and complete the transformation process from scratch, from there to rich.
However, the domestic semiconductor industry is globalized as well as globalized. When the international situation changes and the novel coronavirus epidemic approaches, the semiconductor globalization process is also interrupted, and the supply chain is fragmented. Under such a background of anti-globalization, the domestic semiconductor manufacturing industry with high external dependence will naturally be greatly impacted.
Nowadays, the semiconductor supply chain of major countries and regions has begun to embark on a road of anti-globalization: the United States has taken out the Chip Act, and many companies including Intel, Samsung, TSMC, GF and Texas Instruments are building new fabs in the United States; Japan has attracted large semiconductor manufacturers such as TSMC and Micron, while promoting cooperation with IBM and Rapidus to promote the development of 2nm process technology; Europe has also introduced a corresponding chip bill to double the current 10% global semiconductor market share before 2030.
At the same time, these countries have issued semiconductor restrictions on China, up to the United States, down to Japan, small chips, large equipment, all are included in the scope of control, domestic semiconductor companies have a kung fu but difficult to play.
It is no wonder that the founder of TSMC, Chang, reiterated in several interviews the view that "globalization is dead", he said that the practice of various controls and entity lists, so that globalization and free trade are dead, he also believes that the "fork" of the global supply chain and anti-globalization have brought about a sharp rise in costs, which has increased the price of chips, but also reduced the popularity of chips.
Under such a situation, the domestic semiconductor can not be built behind closed doors, we must, as Professor Wei said in his speech, firmly take the route of re-globalization, expand the opening up, and let more foreign investment in the common development of semiconductors.
However, re-globalization is not backed by a broad market and abundant manpower can be carefree, how to attract and retain foreign enterprises under the interference of geopolitical factors, while solving domestic enterprises in technology, equipment and materials worries, is the realistic problem of re-globalization.
Markets and raw materials are both domestic advantages and, if necessary, a countermeasure to re-globalization.
In 2022, the global gallium market size reached 2.046 billion yuan (yuan), the Chinese market size of 777 million yuan, the global germanium market size is relatively small, only 1.615 billion yuan in 2022, in the segmsegmed semiconductor field will only be less, both indeed can not be compared with hundreds of billions of dollars of semiconductor market.
But they can indeed leverage the market of hundreds of billions of dollars, the reason is not its importance, but a kind of globalization of thinking and behavior inertia, the United States and Japan for decades to enjoy low-cost Chinese raw materials, is one of the benefits of globalization, and the United States CPU, DRAM, Japan's NAND, CMOS can be sold in China, It is also one of the effects of globalization.
As long as the countries enjoying the convenience of globalization can not really stay out of it, whether it is anti-globalization or deglobalization, just use their own influence in globalization, use the means of globalization, to achieve the purpose of non-globalization, in this process, They are more susceptible to external factors.
Looking at the world, the soil of re-globalization is everywhere, while the anti-globalization is cultivated in the greenhouse, whose future is more robust, it has long been self-evident.
Where will there really be a semiconductor industry that jumps out of the three boundaries and is not in the five lines?